Challenges in the hydraulic simulation of slurry transportation through pipelines
The transport of solid particles in a gaseous or l iquid carrier fluid, usually referred to as slurry transport, is an import - ant technology in various industrial fields. Examples for slurry usage are dredging and mining processes, fer tilizer and cement production, desalination plants, the food and paper industry, sewage disposal and agriculture. Slurries can be transported through pipelines continuously over long distances, offering a viable alternative to conventional bulk materials transport options such as conveyor band systems, road and rail.
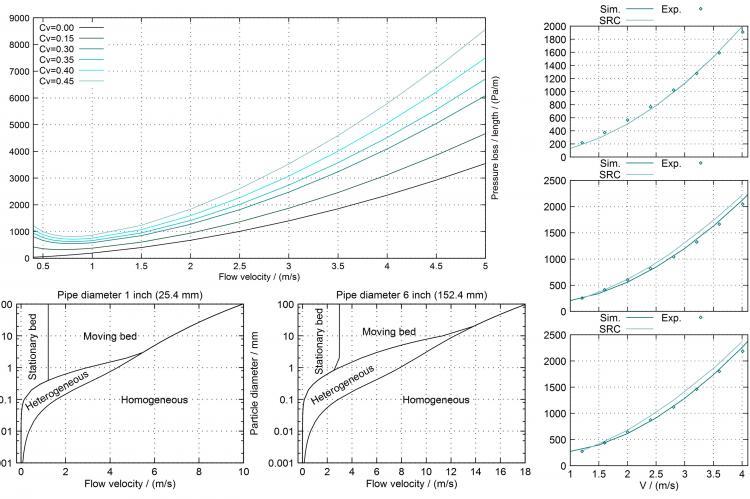
Compared to single-phase flows, which can be described quite well wi th modern simulation tools, slurry flows come along with additional physical phenomena which make precise modelling very challenging. Examples are the settling of slurry particles, which is difficult to describe and can cause unstable flow pat terns, and the non-Newtonian viscous behavior of the carrier fluid if a large concentration o f small slurry particles is dispersed. Therefore, a detailed understanding of the specific physical features of slurry transport is essential for a proper design of sl urry transport pipelines.
The article will give a general over view of the categorization of slurry flows into different flow regimes like the (pseu - do) homogeneous, heterogeneous and deposition flow regime and the dependency of the occurring flow regime on flow velocity, solid concentration, particle and pipeline diameter. In addition, modelling aspects of the different presented flow regimes are given. Understanding rheology and fluid flow is prer equisite for the development of hydraulic simulation tools and to slurry system design and operation.
Here, the authors provide an overview of the chal lenges and approaches in the hydraulic simulat ion of different slurry pipeline systems, as well as a comparison of simulation results obtained with the authors software against examples from the literature are shown.

